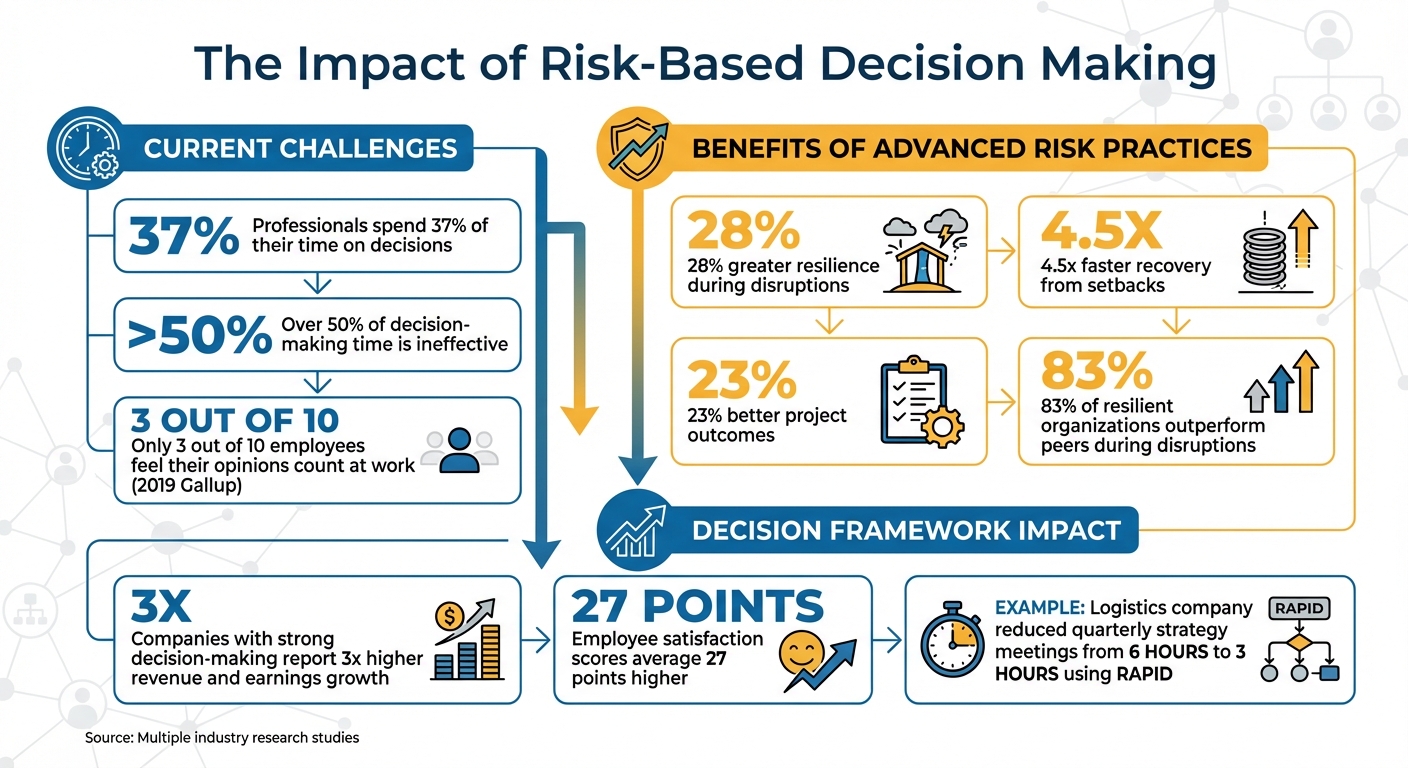
Risk-based decision-making (RIDM) combines qualitative and quantitative risk data to make better choices, balancing challenges and opportunities. Aligned teams using RIDM achieve higher efficiency, resilience, and faster recovery during disruptions. Yet, many professionals spend 37% of their time on decisions, with over half of that time being ineffective.
To improve decision-making, leaders should:
- Set clear, risk-aligned goals: Involve teams early to prioritize risks and establish measurable objectives.
- Use structured frameworks: Tools like RAPID and RACI clarify responsibilities, reduce confusion, and speed up decisions.
- Promote open communication: Psychological safety encourages team input and reduces blind spots.
- Train teams effectively: Practical exercises and scenario planning build confidence in handling risks.
- Track progress: Use Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) and metrics like decision speed to measure success.
Organizations with advanced risk practices report 28% more resilience and recover 4.5 times faster from setbacks. By integrating these approaches, you can transform risk management into a competitive advantage.
Risk-Based Decision Making: Key Statistics and Framework Benefits
Risk-Based Decision Making
sbb-itb-bc03425
Setting Risk-Aligned Goals
Leaders need to convert critical risk priorities into clear and actionable goals. Without this clarity, teams might focus on less important tasks while leaving major risks unaddressed.
Involving teams early in the goal-setting process is key. When team members actively participate in shaping the goals they are expected to meet, they are more likely to take ownership of the outcomes. Collaborative goal-setting creates genuine commitment rather than mere compliance. Leaders who empower those closest to the technical work to make decisions build stronger trust and collective accountability. This approach lays the groundwork for prioritizing risks and creating measurable objectives.
Identifying Risk Priorities
Once goals are aligned, the next step is pinpointing risks that could impact these objectives. Start by clarifying organizational priorities. Bring in cross-functional teams from areas like legal, IT, operations, and compliance to ensure a broad range of perspectives and avoid groupthink.
A practical tool for this is the 5×5 risk matrix, which evaluates risks based on their likelihood and impact. For a more detailed approach, some organizations use the Risk Priority Number (RPN) method, which adds detectability as a third dimension (RPN = Likelihood × Impact × Detectability). Leaders should also set clear escalation thresholds, such as defining numeric scores that require executive review. For instance, any risk scoring above 16 on a 5×5 matrix might automatically be escalated to the risk committee.
"Risk prioritization isn’t just about heat maps and scoring. It’s a business-critical filter that determines which red flags are addressed and which are ignored." – Protecht
Visual tools like the "Doomsday Clock" for risks or "Karma Day" for opportunities can help teams focus on what matters most.
Creating Measurable Goals
After identifying priorities, it’s time to turn them into SMART goals: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-based. Avoid vague targets like "improve security." Instead, aim for precision. For example: "Reduce the average time to detect security incidents from 48 hours to 12 hours by September 30, 2026."
Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) act as early warning systems, helping teams monitor whether risks are within acceptable limits. Pairing KRIs with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) provides a fuller picture by showing both risk exposure and the effectiveness of controls. For example, a spike in customer churn might signal a need to reassess product quality risks.
| Criteria Category | Example Metric | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Revenue lost per hour of downtime | Economic impact of operational risks |
| Operational | Average time to remediate threats | Effectiveness of internal defenses |
| Customer-Facing | Service outage duration | Impact on brand reputation and retention |
| Compliance | Number of regulatory gaps | Adherence to legal requirements |
Encourage team members to set personal milestones that align with broader objectives. This fosters accountability and keeps everyone on track. Tools like "Investors and Help Wanted" boards can also help teams rank risks in a more intuitive way rather than relying solely on numbers.
"Valuing participation and shifting power downward fits extremely well with the empowered teams and servant leadership model promoted by agile methods." – Mike Griffiths, Project Management Professional
Finally, connect goals to measurable business outcomes. For instance, instead of saying "resolve 95% of vulnerabilities within 30 days", frame it as "prevent an estimated $2.3 million in potential breach costs annually." Quantifying the financial benefits of avoided risks, such as breaches or compliance fines, often helps secure faster budget approvals. This approach keeps teams focused and supports dynamic, risk-based decision-making.
Using Structured Decision Frameworks
When risk goals are clearly defined, structured decision frameworks can simplify team responsibilities and speed up execution. High-stakes decisions often stall when roles are unclear. Frameworks like RAPID and RACI eliminate this ambiguity by defining who gathers data, who has veto power, and who ultimately makes the decision. These frameworks build on earlier discussions about goal clarity and risk prioritization, ensuring every step of the decision-making process is assigned to the right person. Companies that consistently make and execute strong decisions report revenue and earnings growth more than three times higher than their competitors. On top of that, their employee satisfaction scores average 27 points higher.
These frameworks are most effective for decisions that are high in value, frequency, or complexity. Applying them to every minor decision isn’t practical. If a decision feels too large to manage, break it into smaller parts. For instance, instead of treating "Digital Strategy" as a single decision, divide it into manageable components like "Channel Strategy" and "In-store Strategy". This method makes it easier to assign roles and avoid bottlenecks.
"Good organizational design creates boundaries for decision authority. Seen in a negative light, this might appear to be establishing ‘turf boundaries’, but in a positive light, it helps clarify accountability." – John May, Co-Founder, The Uncertainty Project
Single-point accountability is key. It ensures everyone knows their role, allowing teams to act faster and with greater confidence, while reducing internal conflicts. Keeping a documented record of the process in a shared location also preserves the rationale behind decisions, which can be invaluable for future learning.
Applying RAPID for Risk-Based Decisions
The RAPID framework breaks decision-making into five distinct roles: Recommend, Agree, Perform, Input, and Decide. The process flows in this order: Recommend → Input → Agree → Decide → Perform.
- Recommend: Drives the process by collecting data and creating a proposal.
- Input: Involves stakeholders who will be impacted, ensuring risks and downstream effects are considered.
- Agree: Reserved for those who must sign off, such as legal or regulatory experts, to ensure compliance.
- Decide: A single individual makes the final call and allocates resources, ensuring clear accountability and avoiding delays.
- Perform: Executes the decision promptly.
Take Intel’s Embedded and Communications Group as an example. In April 2012, conflicts between marketing and product leads caused delays in their roadmap. General Manager Doug Davis reassigned roles, giving the strategic-planning manager the Decider role for the roadmap and assigning product managers as Input providers. This change eliminated inefficiencies and sped up decision-making. Similarly, a logistics company in the Asia-Pacific region implemented RAPID training for its teams in May 2024. This reduced the time spent in quarterly campaign strategy meetings from six hours to three.
| RAPID Role | Responsibility | Impact on Accountability |
|---|---|---|
| Recommend | Gathers input and develops the proposal | Drives the process; acts as the primary worker |
| Input | Provides expertise, facts, and data | Enhances decision quality through diverse perspectives |
| Agree | Signs off on the recommendation | Ensures compliance with mandatory requirements |
| Decide | Makes the final call and commits resources | Provides single-point accountability for the outcome |
| Perform | Executes the decision once made | Ensures timely transition from decision to action |
Clarifying Responsibilities with RACI
While RAPID focuses on decision-making, the RACI framework is better suited for structuring daily tasks and maintaining team alignment. RACI stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed:
- Responsible: The person who performs the work.
- Accountable: The individual ultimately answerable for the task’s success.
- Consulted: Those who provide input or expertise.
- Informed: Stakeholders who are kept updated on progress.
For example, when rolling out a new cybersecurity protocol, the IT security team might be Responsible for system configuration, the Chief Information Security Officer Accountable for the outcome, the legal team Consulted on compliance, and department heads Informed about the rollout schedule. By directly tying each role to specific outcomes, RACI ensures everyone knows their part in achieving the goal.
While RACI focuses on task execution, RAPID zeroes in on decision authority. Together, these frameworks reduce confusion and ensure every stakeholder understands their role, influence, and responsibilities – essential for aligning teams around risk-based decisions.
Building Open Communication and Psychological Safety
After defining roles with tools like RAPID and RACI, the next challenge is ensuring your team can use these frameworks effectively. This is where psychological safety plays a crucial role. Psychological safety is the belief that team members can voice ideas, concerns, or even admit mistakes without fear of punishment or embarrassment. Google’s Project Aristotle, conducted in the early 2010s, highlighted that high-performing teams excel not because of individual IQ or credentials but because they embrace risks through open communication and psychological safety. When a team feels secure, they see risks as chances to grow instead of threats to avoid.
Creating psychological safety starts with leadership. Leaders need to set the tone by being transparent. If you don’t explain the reasoning behind your decisions or admit when something might not work, your team is unlikely to do the same. A 2019 Gallup poll revealed that only 3 out of 10 employees strongly feel their opinions count at work. This gap represents a missed opportunity to address risks before they escalate into bigger problems. Open communication strengthens the decision-making frameworks you’ve already established.
Encouraging Transparent Dialogue
Transparent dialogue thrives on regular check-ins, where team members feel safe discussing concerns without fear of backlash. During these check-ins, asking open-ended questions like, "What perspective are we overlooking?" can uncover hidden insights. This approach helps counter the "sunflower effect", where employees simply align with the leader’s views instead of offering genuine input.
Leaders should also reframe mistakes as learning opportunities. Share your own missteps openly and treat team errors as lessons rather than failures. For instance, Amazon’s leadership principle – "Leaders are never done learning and always seek to improve themselves" – allowed the company to adapt quickly during the COVID-19 pandemic by empowering teams to make informed, risk-based decisions.
Adapt your facilitation style to your team’s experience level. If you’re working with a less experienced group or setting ground rules for risk discussions, a Directive style works best. For seasoned teams tackling tasks like SWOT analysis, a Collaborative approach is more effective. And when gathering input from experts or reviewing lessons learned, a Supportive style encourages quieter team members to contribute while preventing dominant voices from taking over. These methods build transparency and lay the groundwork for deeper psychological safety.
Building Psychological Safety
Defining roles with frameworks like RAPID and RACI is just the beginning. Fostering psychological safety takes things further by improving risk-based decision-making. Psychological safety evolves through four stages: Inclusion Safety (feeling a sense of belonging), Learner Safety (comfort in asking questions), Contributor Safety (confidence in taking ownership), and Challenger Safety (freedom to dissent without fear). A study of nearly 300 leaders over 2.5 years found that teams with high psychological safety performed better and experienced less interpersonal conflict.
To progress through these stages, introduce formal challenge mechanisms for key decisions. Use "devil’s advocate" sessions or red-teaming exercises to stress-test plans. After incidents, focus on systemic learning rather than assigning blame. For example, after a cybersecurity breach, ask, "What process failed?" instead of "Who made the mistake?" This approach encourages honest reporting and reduces the likelihood of hidden risks.
"Psychological safety nurtures a culture where risks are seen as opportunities for growth and innovation, rather than threats to be avoided." – Julien Haye, Author of The Risk Within
Leaders should also practice individuation by treating employees as individuals during one-on-one meetings, allowing them to express unique needs and areas for support. Anonymous risk escalation tools can also help employees bypass management barriers and share critical insights directly. However, it’s not enough to just listen – when someone raises an issue, act on it. Failing to follow through erodes trust, and team members may stop sharing ideas, leaving potential risks unaddressed.
| Stage of Safety | Activity | Practical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Inclusion Safety | Risk Identification | Involve frontline teams and underrepresented groups in discussions about potential risks. |
| Learner Safety | Incident Reviews | Create environments where failures are analyzed for systemic improvements, not blame. |
| Contributor Safety | Control Ownership | Use RACI models to empower individuals with the tools and authority to manage risks. |
| Challenger Safety | Board Reporting | Encourage respectful dissent during debates on risk appetite and strategic planning. |
Training Teams and Monitoring Progress
Training builds on the foundation of psychological safety, transforming potential into actionable results. It’s not enough for your team to feel comfortable speaking up – they need the tools to assess risks systematically and the ability to measure whether their evaluations lead to improved outcomes. Organizations with advanced risk management systems report 28% greater resilience during disruptions and achieve 23% better project outcomes. Bridging the gap between understanding risk assessment and executing it effectively requires structured training and consistent metrics.
Training for Risk Evaluation
Risk training should extend beyond theoretical concepts and dive into hands-on, practical exercises that mimic real-world challenges. Activities like war gaming, competitive simulations, and tabletop exercises allow teams to practice decision-making under pressure. For example, instead of simply discussing supply chain risks, run a scenario where a supplier suddenly declares bankruptcy, forcing teams to juggle cash flow issues and customer commitments. These immersive exercises build the confidence needed to make tough calls in uncertain situations.
Another critical focus area is scenario planning. Teams should learn to frame uncertain decisions, identify key assumptions, and translate those into measurable financial impacts. The goal isn’t to predict the future with precision but to create an early-warning system by preparing for multiple potential outcomes. Proficiency with tools like heat maps, 5×5 risk matrices, and data analytics platforms is essential for visualizing and prioritizing risks effectively.
Beyond initial training, ensure skills are retained and applied through Verification of Competency (VOC) programs. These confirm that team members can perform specific tasks safely and effectively in real-world conditions, not just in theory.
"Risk-based decision-making provides a structured framework for evaluating the potential consequences and benefits of each choice, leading to more informed and strategic decisions." – Ramon Meris, SafetyCulture
Start small with pilot projects to prove the value of training before scaling across the organization. This method reduces resistance by demonstrating results rather than relying on abstract promises. Embed just-in-time training within risk management tools to provide immediate, practical guidance. For example, include prompts or tutorials within software platforms to help users apply what they’ve learned in real-time. Documenting decisions in a centralized log creates a valuable reference library, reinforcing accountability and continuous learning.
Monitoring Alignment Metrics
Training alone doesn’t guarantee success – it’s the measurement that ensures progress. Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are essential for tracking shifts in risk levels and providing early warnings for proactive intervention. Unlike traditional KPIs, which focus on past performance, KRIs are forward-looking. For instance, if KRIs reveal an increase in supplier payment delays, you can address the issue before it disrupts operations.
Using the risk evaluation tools outlined earlier, you can measure how well your team adapts to challenges. Metrics like decision speed and adaptive capacity gauge how quickly your organization responds to disruptions. Companies with structured resilience frameworks recover 4.5x faster from setbacks. Additionally, tracking the frequency of recurring incidents can highlight whether your organization is learning from past mistakes or falling into the same traps.
Another useful metric is the perception gap – the difference between how workers and leaders view risks. This helps assess whether risk management programs are understood and implemented as intended.
| Metric Category | Key Indicators | What It Measures |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Intelligence | Critical Risk Awareness Score, Control Awareness Score | Workforce understanding of risks and controls |
| Operational Resilience | Recovery Speed, Decision Velocity | Ability to adapt and return to normal operations |
| Alignment & Culture | Worker-Leader Perception Gap, Culture Pulse Survey Results | Consistency in risk understanding across levels |
| Program Effectiveness | Reduction in Recurring Incidents, KRI vs. KPI Variance | Impact of risk initiatives on outcomes |
Tools like culture dashboards and pulse surveys can help diagnose your current risk culture and track how leadership behaviors influence employee engagement. Standardizing methodologies – such as creating consistent definitions for risk impact and likelihood – is also critical. Without this, departments may produce conflicting results, complicating decision-making at the executive level.
Ultimately, the goal is for all stakeholders to view risk assessments as practical tools that enhance decision-making across the organization. By combining targeted training with robust measurement practices, teams can stay aligned and ready to tackle emerging challenges effectively.
Using Resilient Power‘s Science-Based Solutions

Making decisions aligned with risk requires solid frameworks and dependable tools. Resilient Power steps in with science-backed solutions that seamlessly integrate into these frameworks. By blending AI-driven technology with tailored methodologies, they help leaders enhance resilience, align teams, and tackle complex risks with precision.
A key element of their approach is vertical development. Instead of merely adding technical skills, this method focuses on expanding a leader’s ability to handle complexity and uncertainty. The idea is simple but powerful: effective risk management begins with leaders who can face ambiguity with confidence. Strengthening this capability lays the groundwork for organizations to perform consistently, even during disruptive times.
Their AI risk platforms leverage machine learning and NLP to identify emerging risks and analyze incident reports. These tools automate critical processes like risk scoring, creating heat maps, and generating dashboards, while also sending alerts when thresholds are crossed. With these capabilities, teams can transition from reactive crisis management to proactive risk strategies, fostering a mindset that focuses on opportunities. Companies using these platforms consistently achieve better outcomes in disruption management and project delivery, with tangible gains in resilience and recovery speed.
In addition to their tech solutions, Resilient Power offers hands-on learning programs designed to align strategy with measurable results. These customized programs help teams connect overarching strategic goals to specific performance indicators, ensuring that everyone understands how their role contributes to success. The training incorporates executive communication, incident response, and actionable strategies, equipping teams to make swift and confident decisions.
Drawing on their global experience with Fortune 500 companies and tech startups, Resilient Power provides insights that work across industries. Their emphasis on team alignment ensures risk management becomes a natural part of daily operations. This approach has proven effective – 83% of resilient organizations outperform their peers when facing disruptions.
Conclusion
Bringing teams together for risk-informed decision-making is an ongoing process that demands regular fine-tuning. It all starts with setting clear, risk-aligned goals that tie directly to your organization’s strategic priorities. This connection forms the backbone for using structured frameworks and fostering continuous improvement.
Frameworks like RAPID and RACI provide teams with the consistency they need to make decisions confidently and efficiently. But these tools alone aren’t enough. Success hinges on open communication and fostering a culture of psychological safety. Teams perform best when members feel empowered to voice concerns, challenge assumptions, and share insights without hesitation. When accountability is shared across the team, risk management evolves from being a top-down directive into a collaborative effort.
To stay prepared for emerging challenges, ongoing training and real-time monitoring through Key Risk Indicators (KRIs) are essential. Research shows that organizations with advanced risk management capabilities not only bounce back faster during disruptions but also consistently outperform their competitors.
Resilient Power’s science-backed methodologies and expert support take this a step further. Their AI-driven platforms and tailored training programs help leaders manage complexity while ensuring teams turn strategic goals into actionable outcomes.
Achieving long-term resilience requires every piece of the puzzle to work together. By embedding clear objectives, reliable frameworks, transparent communication, continuous learning, and expert guidance into daily operations, leaders can ensure risk-informed decision-making becomes a core strength of their organization.
FAQs
How do we decide which risks to address first?
To tackle risks effectively, start by assessing their potential impact and likelihood. Tools like risk matrices or scoring systems can simplify this process. By zeroing in on high-priority risks, you can allocate resources where they matter most.
Taking a data-driven approach is key. Consider factors such as the scale of impact and how risks might interconnect. This helps pinpoint threats that could derail your strategic objectives.
Embedding risk management into your planning process and promoting a risk-aware mindset across your organization ensures decisions are proactive and consistent – laying the groundwork for long-term stability.
When should we use RAPID vs. RACI?
RAPID and RACI are both tools designed to clarify roles, but they focus on different aspects of teamwork and management.
Use RAPID when you need to streamline decision-making. It defines specific roles like who recommends, approves, performs, inputs, and decides. This framework works best for high-stakes decisions where speed and clear accountability are crucial.
On the other hand, RACI is more effective for assigning responsibilities in tasks or projects. It identifies who is Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. This approach is ideal for ongoing processes or projects where roles are distributed across a team.
How do we measure if RIDM is working?
To gauge how well Risk-Informed Decision-Making (RIDM) is working, focus on whether risks are being properly identified, assessed, and addressed in a way that supports your organization’s goals. Some key signs of success include tracking residual risk levels, ensuring outcomes align with the organization’s risk appetite, and leveraging risk assessments to shape decision-making.
You can also evaluate the effectiveness of your risk management processes and compare your organization’s risk intelligence against industry standards. These steps help confirm that RIDM is fostering resilience and enabling thoughtful, risk-aware decisions throughout the organization.



